Synthetics, Simulants & Treatments
Synthetic gems are those made in a laboratory with the same basic chemical composition as a natural gem. Simulants are other gems and materials used to imitate a natural gemstone. Treatments are various processes that natural gem material might undergo in order to improve color, clarity, or stability. Want to know more about these fascinating scientific processes as they apply to gemstones? Select from the Synthetics, Simulants, & Treatments pictorial glossary below to delve into this scientific underworld of gemstones.
Vignettes
Further Resources Gems & Gemology: The Quarterly Journal of The Gemological Institute of America. March-April 1935, Synthetic Diamonds, Historic and Modern, by Anderson, p. 213, 4pp. Winter 1938, Supposed Synthetic...
Enhancement, when used in gemological conversation, stands for a man-induced treatment that improves the appearance or durability of a gemstone. Gem minerals are rare, durable, and beautiful by definition; this...
Terms & Definitions
QUICK LINKS:
Show
Alexandrite-like refers to the ability of a gem material to change colors when viewed under different light sources such as daylight and incandescent lighting. It is named after the natural “change of...
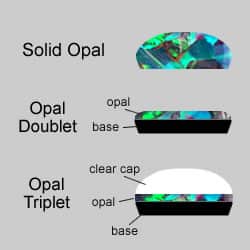
Composite stones are gem simulants that are composed of several materials. Doublets and triplets are good examples. Composite stones are often produced to deceive, but, as in the case of opal, it’s also...
Coque de perle, from the French for ‘pearl shell’ was a Georgian faux pearl carved from the East Indian nautilus shell. The central whorl of the convex part of the...
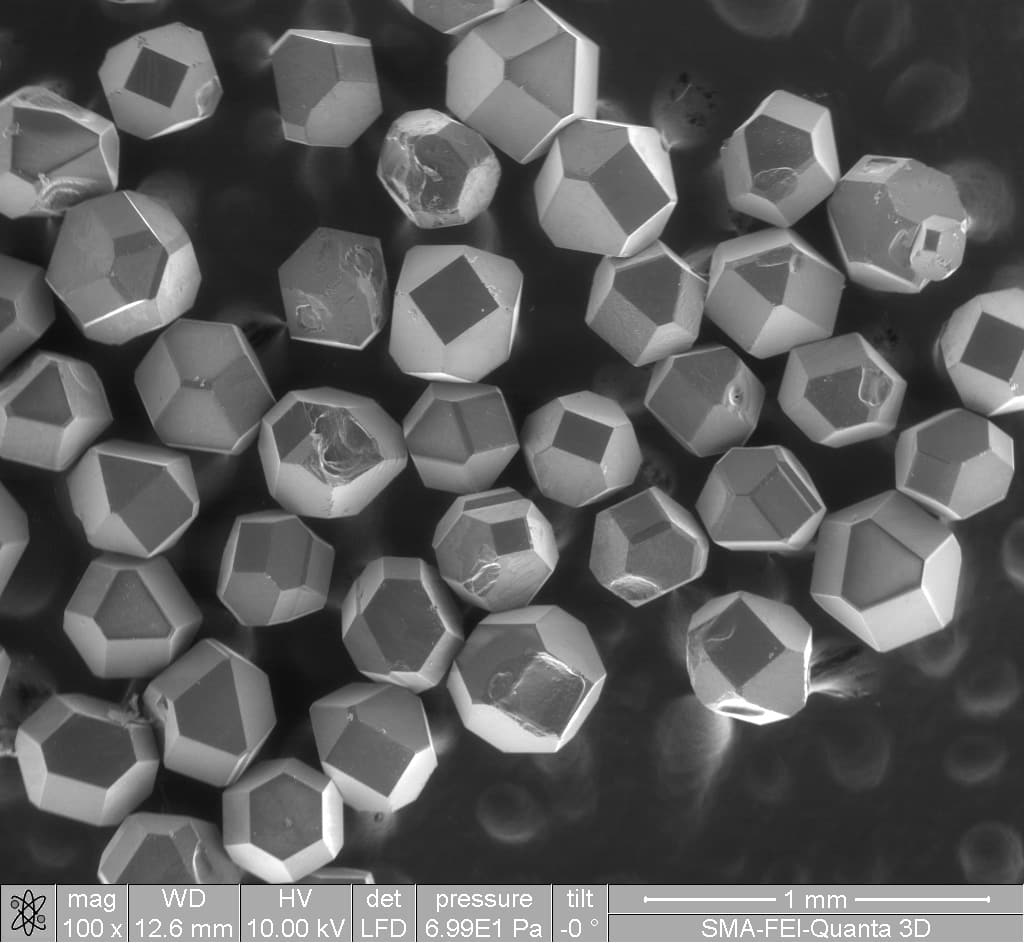
Cubic zirconia is a man-made material used to imitate diamond and other gemstones commonly referred to as CZ. Cubic Zirconia has a thermal insulating property while diamond is a very efficient thermal conductor....
The Czochralski method, developed by Polish scientist Jan Czochralski, was a byproduct of his investigation into the crystallization rates of metal. He accidentally dipped his pen into molten tin, instead...